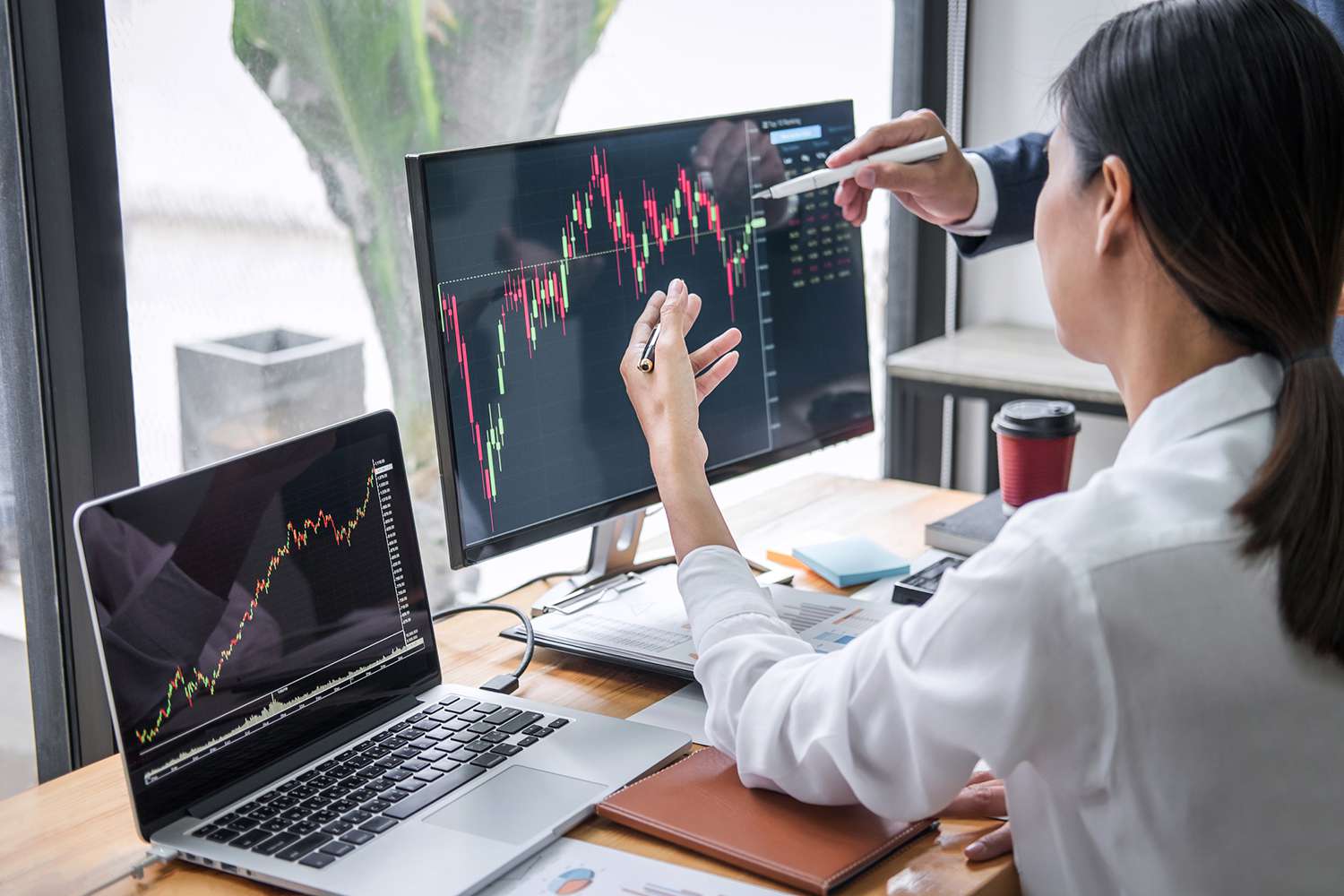
Swing trading, often hailed as the art of capitalizing on short-term market movements, is a strategy that has caught the attention of investors seeking to make quick and substantial profits. This article will provide you with a complete understanding of swing trading, including key principles, techniques, and expert insights to help you succeed in this dynamic and exciting venture.
Swing Trading Demystified
Maximizing Profits with Short-Term Moves may sound complex, but at its core, it’s a relatively straightforward strategy in the world of investing. Let’s break it down:
Swing Trading is a style of trading in which investors aim to capture short to medium-term price movements in financial instruments. Unlike long-term investors who may hold assets for years, swing traders typically hold their positions for a few days to weeks. The goal is to profit from the “swings” or fluctuations in asset prices, making it an enticing option for those looking to capitalize on market volatility.
The Essence of Timing
Timing is everything in swing trading. To maximize profits, you need to buy low and sell high, or sell high and buy low. It’s all about identifying entry and exit points with precision. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Recognizing Trends and Patterns
Successful swing traders master the art of recognizing trends and patterns in the market. This involves analyzing price charts, such as candlestick patterns, and identifying potential entry and exit points.
2. Technical Analysis
Technical analysis plays a vital role in swing trading. It involves using various indicators and tools to predict price movements. Common technical analysis tools include Moving Averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands.
3. Fundamental Analysis
In addition to technical analysis, some swing traders incorporate fundamental analysis. This involves studying financial statements, economic indicators, and news events to make informed decisions.
Strategies for Success
No two swing traders are exactly alike, and various strategies can be employed to maximize profits. Here are some popular approaches:
Breakout Trading
This strategy involves identifying key price levels, or “support” and “resistance” levels, and placing trades when the price breaks through these levels. It’s all about capitalizing on sudden price movements.
Trend Following
Trend following is a popular swing trading strategy that involves identifying and capitalizing on market trends. Swing traders who utilize this method seek to profit from the momentum of assets, buying when the market is in an uptrend and selling when it’s in a downtrend. This strategy relies on the premise that trends, once established, tend to persist for a certain period, allowing traders to ride the wave of price movements.
| Strategy | Key Characteristics | When to Use |
| Trend Following | – Buys in uptrends and sells in downtrends. – Relies on market momentum. – Aims to capture sustained price movements. | – Use when a clear market trend is established. – Effective in stable or trending markets. – Requires patience to ride out trends. |
| Breakout Trading | – Identifies key price levels for entry and exit. – Capitalizes on sudden price movements. – Involves risk of false breakouts. | – Applicable when market volatility is expected. – Useful in markets with well-defined support and resistance levels. – Requires quick decisions. |
| Counter-Trend Trading | – Takes a contrarian approach, looking for trend reversals. – Profits from short-term price corrections. – Risky during strong trends. | – Suitable when a trend reversal is anticipated. – Effective in volatile markets with frequent reversals. – Requires precise timing and risk management. |
| Range Trading | – Thrives in sideways markets, buying at the bottom and selling at the top. – Low-risk strategy when volatility is low. | – Appropriate when the market lacks clear trends and moves in a sideways range. – Effective for risk-averse traders. – Requires patience in ranging markets. |
Counter-Trend Trading
Counter-trend swing traders take a contrarian approach. They look for reversals in market trends and profit from short-term price corrections.
Range Trading
Range traders thrive in sideways markets, buying at the bottom of a range and selling at the top. It’s a low-risk strategy when market volatility is low.
Risk Management
While swing trading can be highly profitable, it’s not without risks. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
▪ Set Stop-Loss Orders
- To protect your capital, it’s crucial to set stop-loss orders. These automatically trigger a sale when a security reaches a predetermined price, limiting potential losses.
▪ Diversify Your Portfolio
- Diversification is a fundamental principle of risk management. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across different assets to reduce exposure to a single risk.
▪ Risk-Reward Ratio
- Calculating your risk-reward ratio is vital. Determine how much you’re willing to risk for a potential reward and stick to this ratio in your trades.
The Art of Emotional Control
Emotions can be your worst enemy in swing trading. Greed and fear can lead to impulsive decisions that result in losses. Maintaining emotional control is crucial:
Develop a Trading Plan
Developing a trading plan is an integral aspect of swing trading, and it’s often the difference between success and failure. A well-structured trading plan serves as your roadmap, guiding your decisions, managing risks, and ensuring discipline in your trading activities.
Key Components of a Trading Plan
A comprehensive trading plan typically includes the following elements:
- Trading Goals: Start by defining your financial objectives. What do you aim to achieve through swing trading? Whether it’s consistent profits, capital preservation, or portfolio growth, your goals should be clear and measurable.
- Risk Tolerance: Determine how much risk you are willing to take in each trade. This should align with your overall financial situation and comfort level. Set a risk percentage per trade, and stick to it.
- Asset Selection: Specify the types of assets you’ll trade, such as stocks, currencies, or commodities. Your choice should be based on your knowledge and experience with those assets.
- Entry and Exit Strategies: Define your criteria for entering and exiting trades. This can include technical indicators, fundamental analysis, or specific price levels. Having a clear strategy helps eliminate emotional decision-making.
- Position Sizing: Decide how much capital you’ll allocate to each trade. Position sizing ensures that you don’t overcommit to a single trade, helping to protect your overall portfolio.
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Set specific levels at which you’ll exit a trade, both to limit losses and secure profits. These levels should be determined by your analysis and risk management strategy.
- Trading Schedule: Determine the times and days you’ll actively trade. Creating a schedule helps maintain consistency and prevents overtrading.
- Review and Evaluation: Establish a regular review process to assess your trades, strategies, and overall performance. Adjust your plan based on your findings.
Benefits of a Trading Plan
Creating and following a trading plan offers several advantages:
- Discipline: It enforces discipline in your trading, preventing impulsive decisions based on emotions.
- Risk Management: A well-structured plan helps you manage risks effectively, preserving your capital.
- Consistency: It ensures that your trading approach remains consistent, even in the face of market fluctuations.
- Objective Decision-Making: By following predefined criteria for entry and exit, you eliminate subjectivity in your trades.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular reviews enable you to learn from your experiences and refine your strategies.
Keep Your Emotions in Check
Even when facing losses or gains, maintain emotional equilibrium. Avoid making hasty decisions driven by emotions.